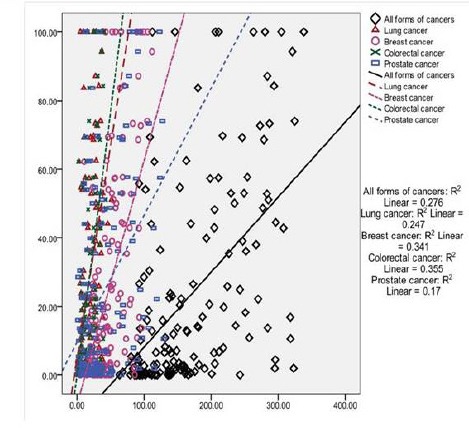
Magnesium deficiency is associated with Parkinson’s disease1, Alzheimer’s disease2, stroke3, migraine4, hypertension, congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, diabetes5, affective disorders like stress6, depression and anxiety7, chronic inflammation, cancer8, and muscle integrity9.
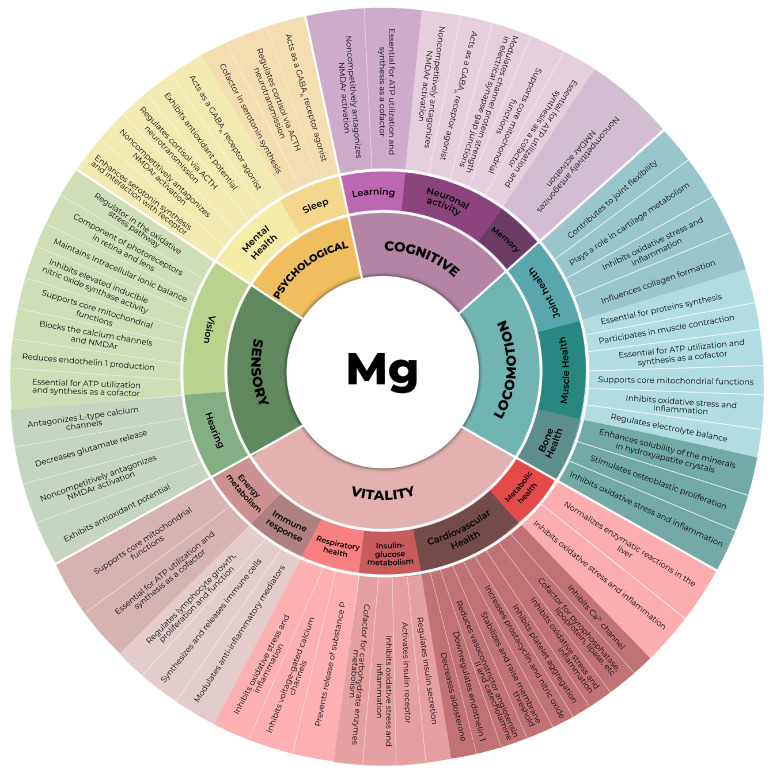
Magnesium also affects all of the hallmarks of aging, which are listed here in yellow and linked to their outcomes in blue:
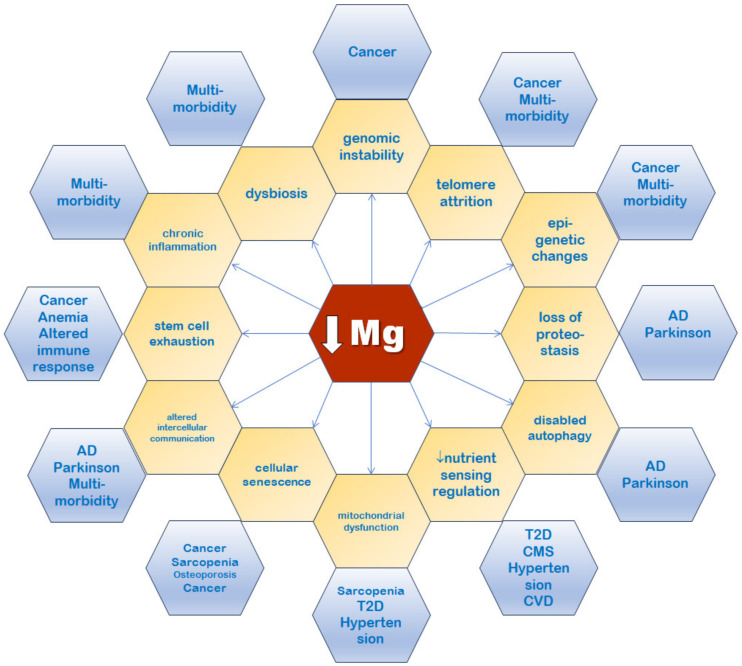
What causes deficiency?
The majority of people in the US are not meeting the RDA for magnesium, with only 43% of people getting enough.10 Magnesium deficiency is also becoming more common over time11.
This is despite nearly a third of all US adults taking multivitamins, which usually include magnesium.12 One reason they can still be deficient in magnesium is that zinc13, calcium14 and vitamin D15 supplementation can block magnesium absorption.
Magnesium is also lost in sweat, which can cause athletes to be deficient16.
Foods that are high in magnesium like whole grains, green leafy vegetables, and nuts are readily available17, but unfortunately popular pesticides and fertilizers reduce the ability of plants to absorb magnesium from the ground18, meaning that in the last 50 years, as pesticide and fertilizer use has increased, magnesium in diets has decreased.
Mg depletion in the soil results in lower concentrations in plants, therefore altering animal intake and resulting in human Mg deficient intake19.
For these reasons, it’s important for most people to supplement magnesium, and to make sure to take it separately from other minerals like zinc, iron, and calcium. The usual recommendation is to allow at least a 2-hour buffer after taking magnesium.20
Magnesium can also affect absorption of certain pharmaceuticals like antibiotics, and diabetes and thyroid medication. If you take prescription medication it’s essential that you familiarize yourself with any contraindications, which are usually listed in the manual or online.
This can be a great way to evaluate the quality of a multivitamin or protocol; if it provides other minerals along with magnesium in the same tablet or time-frame, it might not be the most well-planned product.
Increased calcium and phosphorus intake also increases magnesium requirements and may worsen or precipitate magnesium deficiency.21
When the ratio of magnesium to calcium and phosphorous is outside of the normal range, it leads to various problems known collectively as disorders of mineral metabolism22.
In the last century, phosphorous and calcium intake have generally increased, thanks to processed meat, soft drinks and cheese, while magnesium has decreased.
[…] the most dramatic change that has occurred since the early 1900s until now regarding phosphate, calcium and magnesium has been a reduction in magnesium intake, going from around 500 mg/day to an average of 250 mg/day. Thus, the calcium:magnesium ratio has increased from approximately 2:1 to 5:1, and the phosphate:magnesium ratio has increased from 1.2:1 to around 7:1.23
Best forms of magnesium
Elemental magnesium is not well absorbed on its own, so it needs to be bound with something else to be worth taking as a supplement. There are a lot of popular forms, with some significant differences between them.
One of the most popular forms is magnesium citrate, which is lovingly known to some as magnesium shitrate, because it is an osmotic laxative that doubles as a treatment for constipation. You might want to avoid that for your regular health stack. So what other options are there?
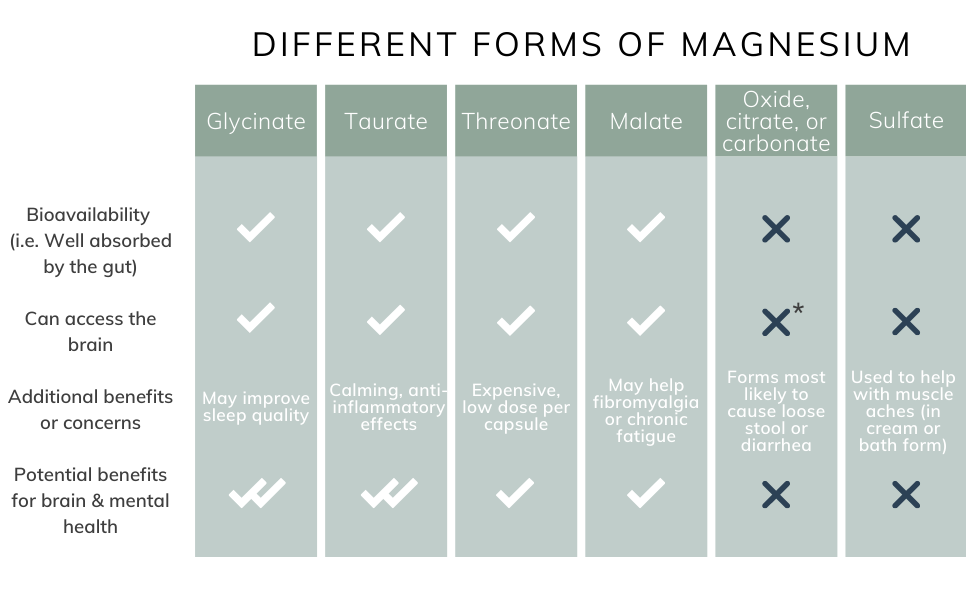
Here we can see some key differences between forms. As you might be able to guess from the words “glycinate” and “taurate”, they are magnesium bound with glycine and taurine, which are both great for health and longevity on their own. They can also both go into the brain, and have been associated with heart health24
How much should I aim to get?
Each form of magnesium has a certain percentage of elemental magnesium, which is that amount of actual magnesium. Ideally those numbers are written on the container so you know you are getting the actual amount you want. The RDAs are based on the amount of elemental magnesium, not the amount of bonded magnesium.
The NIH recommends that in general, adults get between 310-420mg of elemental magnesium per day25.
It’s important to consider individual needs and risks, and for those who are willing and able to measure their blood magnesium levels, that is a more reliable way to know whether you have too little. For example, when treating deficiency:
The therapy should proceed for more than one month, and then continue with a dose that holds the serum value not lower than 0.9 mmol/L magnesium26.
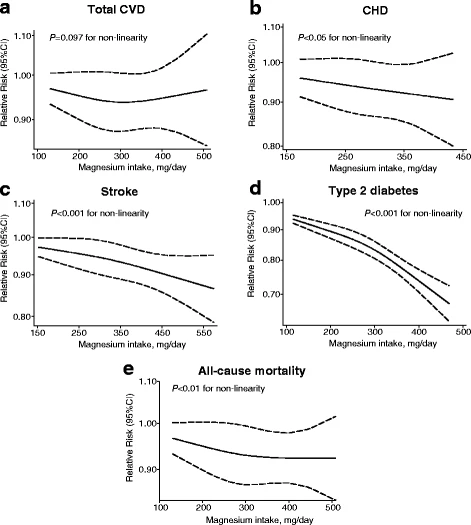
As we can see, magnesium intake reduces risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality. The total cardiovascular disease graph is the only one that is less straightforward, with big gaps between the lines showing a lack of confidence, and the authors of the meta-analysis say:
The pooled results suggest that magnesium intake is not significantly associated with CVD27
Conclusion
I think it would be hard to find another single supplement that has such a profound array of effects, and is such a common deficiency.
Making sure you get 310-420mg per day from all sources, while also not getting too much calcium, zinc and phosphorous, will help you stay healthy and live longer.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29920021/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5660707/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7103847/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11858643/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15372830/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7761127/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7352515/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8349125/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38140385/ ↩︎
- https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeast-area/beltsville-md-bhnrc/beltsville-human-nutrition-research-center/docs/california/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5786912/ ↩︎
- https://edition.cnn.com/2023/04/18/health/supplement-use-wellness/index.html ↩︎
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-Consumer/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14013831/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14268669/ ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2373583/ ↩︎
- https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-016-0742-z#Sec1 ↩︎
- https://hh-ra.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Glyphosate-mineral-levels-EurJAgron-Cakmak-2009.pdf ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7649274/ ↩︎
- https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601074.html ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5786912/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2486454/ ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5786912/ ↩︎
- The Mineral Fix by James DiNicolantonio and Siim Land ↩︎
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/#h2 ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5786912/#s10 ↩︎
- https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-016-0742-z#Sec9 ↩︎